The Need for Robust Web3 Pentesting and Supply Chain Security
Securing the Future of DeFi with Advanced Pentesting, Supply Chain Security, and onchain monitoring (guardrail.ai)
As Web3 continues to revolutionize the digital landscape, offering decentralized solutions and unprecedented user control, it simultaneously exposes new and complex security challenges. The rapid evolution of decentralized applications (dApps), smart contracts, and blockchain technologies has outpaced traditional security measures, making the ecosystem a fertile ground for sophisticated cyber threats.
Protocols are ditching legacy tools for Guardrail's real-time, Web3-native security solution.
Why Guardrail? Less noise, fully customizable monitoring, rapid threat detection, and managed incident response that scales seamlessly.
Book your free Guardrail demo now
The Escalating Threat Landscape in 2025
The first quarter of 2025 has been particularly alarming for Web3 security:
Bybit Exchange Breach: In February, North Korean hacking group TraderTraitor orchestrated the largest cryptocurrency heist to date, stealing approximately $1.5 billion from Bybit, the world's second-largest crypto exchange. The attackers employed advanced spear-phishing techniques and malware to infiltrate the exchange's systems.
Supply Chain Attack on GitHub Actions: A supply chain attack compromised the tj-actions GitHub repository, affecting over 23,000 users. Malicious scripts were introduced, designed to exfiltrate secrets and credentials during automated workflows.
Dormant Malware Activation in E-commerce Platforms: A supply chain attack that lay dormant for six years became active, compromising hundreds of e-commerce sites. The malware, embedded in third-party software, began exfiltrating customer data and payment information.
These incidents underscore a critical reality: attackers are increasingly targeting the interconnected components of the Web3 ecosystem, exploiting vulnerabilities in supply chains and third-party integrations.
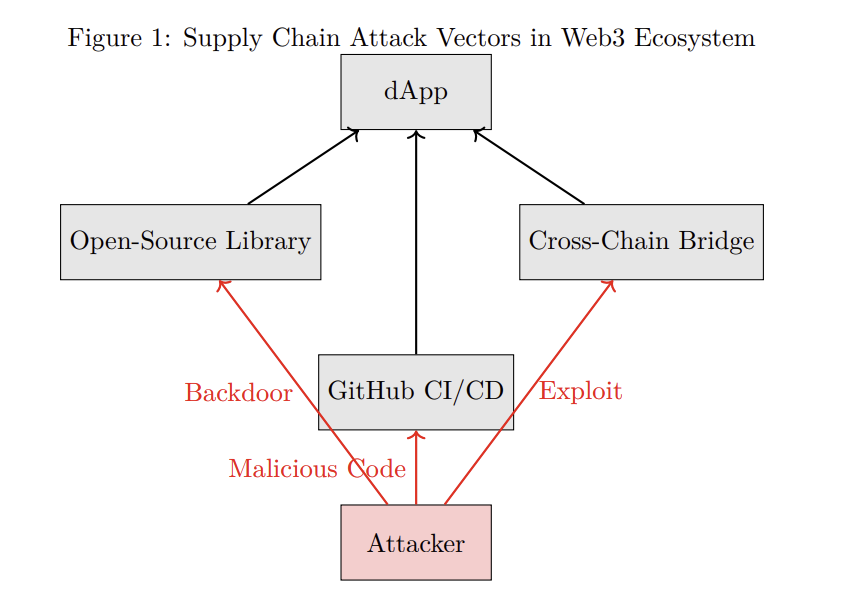
The figure illustrates how attackers exploit trusted dependencies in the Web3 supply chain—such as open-source libraries, cross-chain bridges, and CI/CD pipelines—to inject malicious code, backdoors, or exploits.
By compromising these components, attackers aim to propagate harmful code to decentralized applications (dApps), ultimately targeting users’ private keys, funds, or sensitive data.
Understanding the Unseen Threat Vectors
Web3's decentralized nature introduces unique security challenges:
Third-Party Dependencies: Many dApps rely on open-source libraries and smart contract templates. A vulnerability or malicious code in a single dependency can cascade across multiple projects.
Cross-Chain Bridges: Bridges facilitating interoperability between blockchains are complex and often lack rigorous security audits, making them prime targets for attackers.
Centralized Development Tools: Despite the decentralized ethos, many Web3 projects depend on centralized platforms like GitHub for code management, introducing potential single points of failure.
AI-Generated Code: The increasing use of AI to generate code can inadvertently introduce vulnerabilities, as AI models may not fully comprehend the security implications of the code they produce.
Understanding Supply Chain Attack Vectors in Web3
Supply chain attacks in Web3 exploit the ecosystem's reliance on interconnected components, often aligning with vulnerabilities listed in the OWASP Top 10, such as A06: Vulnerable and Outdated Components and A07: Identification and Authentication Failures.
These attacks target the trust placed in third-party dependencies, tools, and integrations, leveraging weaknesses to infiltrate systems. Specific vulnerabilities and attack methods include:
Dependency Confusion: Attackers upload malicious packages to public repositories like npm or PyPI with names mimicking legitimate ones, tricking developers into downloading them. This can lead to Remote Code Execution (RCE), allowing attackers to run arbitrary code within a project's environment.
API Issues: Poorly secured APIs, a key concern in the OWASP Top 10 (A01: Broken Access Control), are often exploited in Web3 applications. Unprotected API endpoints in dApps or cross-chain bridges can expose sensitive data or allow unauthorized access, enabling attackers to manipulate transactions or steal private keys.
Compromised CI/CD Pipelines: Attackers target CI/CD tools, such as GitHub Actions, to inject malicious scripts during automated builds, as seen in the tj-actions incident. This can result in Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) or credential theft, compromising entire development workflows.
Malicious Dependency Injection: Attackers compromise legitimate open-source libraries or smart contract templates, embedding backdoors or malicious code. This can cascade across multiple dApps, amplifying the attack's impact.
Typo-Squatting: Similar to dependency confusion, attackers create malicious packages with names closely resembling popular libraries, exploiting developer errors during installation.
Dormant Malware in Third-Party Software: As seen in the e-commerce platform attack, malware embedded in third-party software can remain undetected for years, activating later to steal data or disrupt operations.
These vulnerabilities highlight the need for rigorous scrutiny of every component in the Web3 supply chain, from development tools to deployed smart contracts.
The Imperative for Comprehensive Web3 Pentesting
Traditional security audits often fall short in the dynamic and interconnected Web3 environment. A more holistic approach is necessary:
Continuous Monitoring: Implementing real-time monitoring of smart contracts and associated dependencies to detect anomalies promptly.
Supply Chain Audits: Regularly auditing third-party libraries, tools, and platforms for vulnerabilities or malicious code.
Dependency Auditing: Extensive scrutiny of every dependency and integration point.
Threat Modeling: Mapping and simulating potential attack paths through supply chains.
Simulated Attacks: Conducting penetration tests that mimic real-world attack scenarios to identify and remediate vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
Developer Education: Training developers to recognize and mitigate potential security risks in their code and dependencies.
Proactive Threat Detection: Incorporate pentesting and simulation exercises into regular project cycles.
Take Action Today
Ensure your Web3 ecosystem's integrity by proactively addressing these threats. Request a comprehensive Web3 security pentest from our experts: https://www.web3sec.news/supply-chain
Final Thoughts
As Web3 continues to innovate and expand, robust pentesting and stringent supply chain security are no longer optional—they are essential for safeguarding decentralized systems and maintaining user trust worldwide.
./Happy hacking